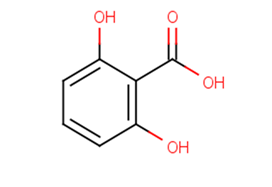
26-Dihydroxybenzoic acid
CAS No. 303-07-1
26-Dihydroxybenzoic acid( —— )
Catalog No. M20573 CAS No. 303-07-1
26-Dihydroxybenzoic acid is a secondary metabolite of salicylic acid which has been hydrolyzed by liver enzymes during phase I metabolism.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 500MG | 38 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name26-Dihydroxybenzoic acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description26-Dihydroxybenzoic acid is a secondary metabolite of salicylic acid which has been hydrolyzed by liver enzymes during phase I metabolism.
-
Description26-Dihydroxybenzoic acid is a secondary metabolite of salicylic acid which has been hydrolyzed by liver enzymes during phase I metabolism.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
RecptorHuman Endogenous Metabolite
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number303-07-1
-
Formula Weight154.12
-
Molecular FormulaC7H6O4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:30 mg/mL (194.65 mM)
-
SMILESOC(=O)c1c(O)cccc1O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference



-
(±)-Propionylcarniti...
(±)-Propionylcarnitine chloride (Propionyl-DL-carnitine chloride) is a mixture of short-chain acylcarnitines used as a dietary supplement for the study of chronic diabetes.
-
2-Ethylpyrazine
2-Ethylpyrazine is present in roasted coffee beans and is a volatile compound .2-Ethylpyrazine induces vasodilation through the activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factors.
-
Propionic acid
Propionic acid (PA) is widely used as an antifungal agent in food. It is present naturally at low levels in dairy products and occurs ubiquitously together with other short-chain fatty acids (SCFA) in the gastro-intestinal tract of humans and other mammals as an end-product of the microbial digestion of carbohydrates.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


